+X*�`}-3�� 简介:
FRED作为COM组件可以实现与Excel、VB、
Matlab等调用来完成庞大的计算任务或画图,本文的目的是通过运行一个案例来实现与Matlab的相互调用,在此我们需要借助脚本来完成,此脚本为视为通用型脚本。
N@Mea���O� -;P��<Q`{I 配置:在执行调用之前,我们需要在Matlab命令行窗口输入如下命令:
g=Q�g��a09 enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
@I�i�T8B�� enableservice('AutomationServer')
M2@q�{R�iS 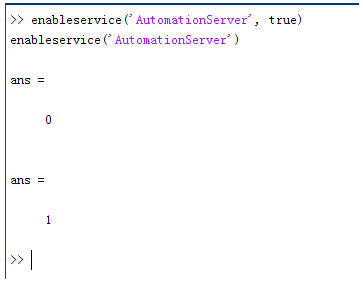 �&�vMH
AZd
�&�vMH
AZd 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于
通信。
4(�aesZ8h K%=n�� \�Y 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤:
l���IF�t�/ 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考.
<Z� m �,q} 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library
�uA���v��s 3. 将名字改为MLAPP
�=|U2 }U;� ZHC sv]l�� G'��Q7�(�c 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。
^CK�)q2K>[ 图 编辑/参考
9uS���7G�* �uPF yRWK� D`t�� e|K5 现在将脚本代码公布如下,此脚本执行如下几个步骤:
_).'SU)��> 1. 创建Matlab服务器。
Q?a"uei�[� 2. 移动探测面对于前一聚焦面的位置。
#h3+T*5} 6 3. 在探测面追迹
光线 �d(�@��A� 4. 在探测面计算
照度 b(S�V_.4,' 5. 使用PutWorkspaceData发送照度数据到Matlab
b<F� 4_�WF 6. 使用PutFullMatrix发送标量场数据到Matlab中
�Pm�1�
"
0 7. 用Matlab画出照度数据
/M3�D[aR<d 8. 在Matlab计算照度平均值
G�wW#Ww;Oc 9. 返回数据到FRED中
pK8nzGQl7 p_z"��U�wp 代码分享:
-ufmp��q. <{�) 4gvH Option Explicit
Mt�YP3:�� uf�;q��/Wr Sub Main
*�2AQ'%�U~ )2FO+_K?�T Dim ana As T_ANALYSIS
Dz50,*�}J� Dim move As T_OPERATION
gNq���V>p� Dim Matlab As MLApp.MLApp
z�JnVO$A'� Dim detNode As Long, detSurfNode As Long, anaSurfNode As Long
��U��n/fP1 Dim raysUsed As Long, nXpx As Long, nYpx As Long
0&.lS�wa Dim irrad() As Double, imagData() As Double, reals() As Double, imags() As Double
_#gsR"�FZ$ Dim z As Double, xMin As Double, xMax As Double, yMin As Double, yMax As Double
�aq���M_t Dim meanVal As Variant
og�\XL�J}_ U2�AGH2emw Set Matlab = CreateObject("Matlab.Application")
5{g9Wh[��� MJG%Hak�K0 ClearOutputWindow
\�a6�)�t%u epbp9[`�� 'Find the node numbers for the entities being used.
>�o�} �ati detNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen")
l�Bn*G&(P� detSurfNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen.Surf 1")
vUK>4^{J5� anaSurfNode = FindFullName("Analysis Surface(s).Analysis 1")
��j�kP70Is 3E��Zw���F 'Load the properties of the analysis surface being used.
+w�UhB\F
* LoadAnalysis anaSurfNode, ana
Q$vr`yV#=6 A�� ��C^[3 'Move the detector custom element to the desired z position.
rl�^�LS��z z = 50
8QN8bGxK � GetOperation detNode,1,move
.cF$f�4>�2 move.Type = "Shift"
c�x,��A.Lc move.val3 = z
Zd(d]�M_x� SetOperation detNode,1,move
S1�zw�'!O5 Print "New screen position, z = " &z
����:'dc=C M([H\^\:�� 'Update the model and trace rays.
I.u,f:Fl'� EnableTextPrinting (False)
Yg�iGI�
<U Update
�lkZC�?--H DeleteRays
oPy� �zk7{ TraceCreateDraw
8@aS9�t�h$ EnableTextPrinting (True)
4)� 3p�a�* na3k��Hx�@ 'Calculate the irradiance for rays on the detector surface.
X{xJ*T y�' raysUsed = Irradiance( detSurfNode, -1, ana, irrad )
�N� �]7a�= Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the irradiance calculation.
SU'1#�$69F ;��0!���Wd 'When using real number data to send to MATLAB, it is simplest to use PutWorkspaceData.
tTFoS[�V� Matlab.PutWorkspaceData("irradiance_pwd","base",irrad)
�x#0�@���$ 4����)�iEj 'PutFullMatrix is more useful when actually having complex data such as with
��{@�� y, 'scalar wavefield, for example. Note that the scalarfield array in MATLAB
qX'a&~s)�n 'is a complex valued array.
k6-n.Rl01� raysUsed = ScalarField ( detSurfNode, -1, ana, reals, imags )
r65��NKiQD Matlab.PutFullMatrix("scalarfield","base", reals, imags )
_�A|��\.(t Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the scalar field calculation."
`7%�eA9*.m ?+O|m�X}`- 'Calculate plot characteristics from the T_ANALYSIS structure. This information is used
LXC`�Zq�\ 'to customize the plot figure.
5SL>q`t.bd xMin = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amin-0.5)
�I*t)x,~3� xMax = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amax+0.5)
��ba9<(0`� yMin = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmin-0.5)
�!;*2*WuO; yMax = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmax+0.5)
�U9�o*6`"o nXpx = ana.Amax-ana.Amin+1
m9�0R8 ��V nYpx = ana.Bmax-ana.Bmin+1
eH�!|MHe�� 6&Q�TVdK'O 'Plot the data in Matlab with some parameters calculated from the T_ANALYSIS
m=��.7f�9� 'structure. Set the axes labels, title, colorbar and plot view.
�h�==G�dS4 Matlab.Execute( "figure; surf(linspace("&xMin &","&xMax &","&nXpx &"),linspace("& yMin &"," & yMax & "," & nYpx & "),irradiance_pwd, 'EdgeColor', 'None');" )
.&x?�`pER� Matlab.Execute( "xlabel('X Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "ylabel('Y Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "zLabel( 'Irradiance' )" )
:ZfUj��qRE Matlab.Execute( "title('Detector Irradiance')" )
'}�`h��Y1v Matlab.Execute( "colorbar" )
0*;�9CH=BE Matlab.Execute( "view(2)" )
:/[Y�Y?pg- Print ""
q�uG��Pk)c Print "Matlab figure plotted..."
�Z)�O>h^0� ���q3-;}+� 'Have Matlab calculate and return the mean value.
<SM&VOiaOz Matlab.Execute( "irrad = mean(mean(irradiance_pwd));" )
uP��=_-ZUW Matlab.GetWorkspaceData( "irrad", "base", meanVal )
9�;Pu9s[q2 Print "The mean irradiance value calculated by Matlab is: " & meanVal
HjK<)��q8b 3:��8n�wt� 'Release resources
Vc52�s+7=8 Set Matlab = Nothing
KO�]?>>5S6
iRwW>�a3/ End Sub
��Rf(x^J�{ Y���eE�xjC 最后在Matlab画图如下:
DET�!br'z5 'T��f#�S@o 并在工作区保存了数据:
x\b�R�j>%( 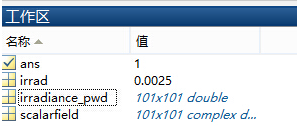 F}B/�-".�^
F}B/�-".�^ 并返回平均值:
D@(�M+u9/% k *;{n8o?) 与FRED中计算的照度图对比:
h�,'mN\6�t �8@W/43K8- 例:
d�I
ZTLb"a ��:�
9?Cm` 此例
系统数据,可按照此数据建立
模型 Y\g�90���� Xq�^�y<��[ 系统数据
�Q"6hD?�6. �vz�yI::f? i3��l ��#~ 光源数据:
9�{UP)17� Type: Laser Beam(Gaussian 00 mode)
'q}��;L��6 Beam size: 5;
�X��|1_0 Grid size: 12;
H�8���<7#� Sample pts: 100;
gLxT6v5wk. 相干光;
J'\eS./w|
波长0.5876微米,
;x�3 ]�4^ 距离原点沿着Z轴负方向25mm。
\;�B$hT7z* q:-��]d0B+ 对于执行代码,如果想保存图片,请在开始之前一定要执行如下代码:
�B�s��u=^z enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
V�:(w\'�wm enableservice('AutomationServer')