-
UID:317649
-
- 注册时间2020-06-19
- 最后登录2025-12-12
- 在线时间1894小时
-
-
访问TA的空间加好友用道具

|
简介:FRED作为COM组件可以实现与Excel、VB、Matlab等调用来完成庞大的计算任务或画图,本文的目的是通过运行一个案例来实现与Matlab的相互调用,在此我们需要借助脚本来完成,此脚本为视为通用型脚本。 �+Z��~!�n� ~'QeN%qadP 配置:在执行调用之前,我们需要在Matlab命令行窗口输入如下命令: SJc@i�ff�S enableservice('AutomationServer', true) gI�M'b�A<~ enableservice('AutomationServer') yP9wY�F^A\ 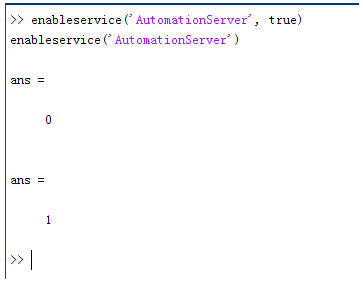 S�@zko�j�@ 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于通信。 UQ�?OD�~7� g74z]Uj.�B 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤: r�jQhU%�zv 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考. S�L�jf<.�S 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library
~
���9~\f 3. 将名字改为MLAPP \j})K�u��l #Q�7x�:,�f OPt;�G,$ta 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。 a(DZGQ-as
DcR�}�pQ(e S�@zko�j�@ 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于通信。 UQ�?OD�~7� g74z]Uj.�B 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤: r�jQhU%�zv 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考. S�L�jf<.�S 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library
~
���9~\f 3. 将名字改为MLAPP \j})K�u��l #Q�7x�:,�f OPt;�G,$ta 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。 a(DZGQ-as
DcR�}�pQ(e 图 编辑/参考 ��-Yj�gS/g <CK�mM�Z�{ 现在将脚本代码公布如下,此脚本执行如下几个步骤: ���kx�q�c6 1. 创建Matlab服务器。 #!�u�5�1P1 2. 移动探测面对于前一聚焦面的位置。 ,\9m�At1O� 3. 在探测面追迹光线 V;hwAQb��F 4. 在探测面计算照度 }��Wche/g` 5. 使用PutWorkspaceData发送照度数据到Matlab ,i�bPSN5Ca 6. 使用PutFullMatrix发送标量场数据到Matlab中 �]b�aaOD$Z 7. 用Matlab画出照度数据 i Kk"j���� 8. 在Matlab计算照度平均值 ~z
_](HKoS 9. 返回数据到FRED中 ���oYh<��k Li����-(p" 代码分享: }�wOpPN�[4 �71/�m.w�� Option Explicit t-7U1B}=<C �6�+B{4OY� Sub Main �o|�;eMO-� YaN�H�.$.: Dim ana As T_ANALYSIS W6Aj�<�{\F Dim move As T_OPERATION �J1]w*�2 Dim Matlab As MLApp.MLApp Tq\~��<rEo Dim detNode As Long, detSurfNode As Long, anaSurfNode As Long X:``{!~geo Dim raysUsed As Long, nXpx As Long, nYpx As Long �Ph��+X{| Dim irrad() As Double, imagData() As Double, reals() As Double, imags() As Double ����)�{��� Dim z As Double, xMin As Double, xMax As Double, yMin As Double, yMax As Double �o!to�O&�= Dim meanVal As Variant h#m:Y~G�oF
�GKyG
#Fl Set Matlab = CreateObject("Matlab.Application") 4O�O�n,�09 G�l8&Fr��R ClearOutputWindow 7�{An@hN�h �=0P�RAc� 'Find the node numbers for the entities being used. ?�)�'�
2l6 detNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen") {� 8f+�h� detSurfNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen.Surf 1") "7��yNKO;W anaSurfNode = FindFullName("Analysis Surface(s).Analysis 1") t���`Y!�"l ![��@T �iM 'Load the properties of the analysis surface being used. R{)
Q1~H=q LoadAnalysis anaSurfNode, ana �/j��' B\, �I�Obx^N_K 'Move the detector custom element to the desired z position. )W1(�tEq59 z = 50 JS�/M~8+Et GetOperation detNode,1,move :/v,r=Y9�p move.Type = "Shift" 1X::�0�;3� move.val3 = z bbNU�\r�5% SetOperation detNode,1,move 2�<'�`^AO@ Print "New screen position, z = " &z v0�A�i!��# $E�i�o$TI� 'Update the model and trace rays. +:>�J�Z$
EnableTextPrinting (False) x*h?%egB!p Update o�e!�:|ck< DeleteRays )�_77>f��% TraceCreateDraw l@N;sI<O�- EnableTextPrinting (True) % �Cu.u)/+ SL�tSq�G7~ 'Calculate the irradiance for rays on the detector surface. 69C8-fF0[I raysUsed = Irradiance( detSurfNode, -1, ana, irrad ) zb5�N,�!%r Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the irradiance calculation. -]Q(~�'�a� n$XdSh/��� 'When using real number data to send to MATLAB, it is simplest to use PutWorkspaceData. I�X<��r5!
Matlab.PutWorkspaceData("irradiance_pwd","base",irrad) _�)K��Y��� dU]i�-N��F 'PutFullMatrix is more useful when actually having complex data such as with a�qs%m�� ( 'scalar wavefield, for example. Note that the scalarfield array in MATLAB k�]?z�~��p 'is a complex valued array. JBR[;
z�M raysUsed = ScalarField ( detSurfNode, -1, ana, reals, imags ) �*�m�e,(�C Matlab.PutFullMatrix("scalarfield","base", reals, imags ) l#D�-q/k?� Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the scalar field calculation." J�F�M"ii{8 ���9<�|m�4 'Calculate plot characteristics from the T_ANALYSIS structure. This information is used �Ys-Keyg�� 'to customize the plot figure. e(�yQKwV�D xMin = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amin-0.5) z,{e]MB)M� xMax = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amax+0.5) #�(%t*"IY; yMin = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmin-0.5) ~{L.��f94N yMax = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmax+0.5) 'h-3V8m^e� nXpx = ana.Amax-ana.Amin+1 fokwW}>B[f nYpx = ana.Bmax-ana.Bmin+1 #��B �@X� 5x8'�K7/4. 'Plot the data in Matlab with some parameters calculated from the T_ANALYSIS Y4mC�_4EU� 'structure. Set the axes labels, title, colorbar and plot view. �aje^Z=��] Matlab.Execute( "figure; surf(linspace("&xMin &","&xMax &","&nXpx &"),linspace("& yMin &"," & yMax & "," & nYpx & "),irradiance_pwd, 'EdgeColor', 'None');" ) �6*��ZU}xT Matlab.Execute( "xlabel('X Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "ylabel('Y Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "zLabel( 'Irradiance' )" ) �Fr-�[UZ~V Matlab.Execute( "title('Detector Irradiance')" ) U~aWG\h#X Matlab.Execute( "colorbar" ) �[tUv*jw�% Matlab.Execute( "view(2)" ) Dp*:Q){>�E Print "" )ll?-FZ
�� Print "Matlab figure plotted..." wms��1IV%; Ko�#4z%�Yq 'Have Matlab calculate and return the mean value. JE0?�@PI�$ Matlab.Execute( "irrad = mean(mean(irradiance_pwd));" ) I-xwJi9?�, Matlab.GetWorkspaceData( "irrad", "base", meanVal ) cDC��J]iDs Print "The mean irradiance value calculated by Matlab is: " & meanVal ��]}P�l%.� $`|5/,M%QN 'Release resources ~}BJ0P(VMc Set Matlab = Nothing }wG,BB�%N 2Ok?@ZdjA{ End Sub q"S(�7xW�S y-�'"� >� 最后在Matlab画图如下:
LI[ ?~P2\ j�����"5Pe 并在工作区保存了数据: lLH$�`Wnv� EYG"49�
�c 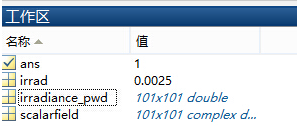 �v��F"��c �v��F"��c
�n!�a<:]b< 与FRED中计算的照度图对比: uJgI<l'|e3 :�/B�:FY�= 例: �Q �uB�+vL �~z5@V5��z 此例系统数据,可按照此数据建立模型 =yo{[�&Jz�
RU�6�KIg{H 系统数据 [g#��s&�bF
[OzzL\)3l� �0�h2�2V�$ 光源数据: V]�rhVMA�� Type: Laser Beam(Gaussian 00 mode) Rp��0|zP,5 Beam size: 5; �yO=p3PV d Grid size: 12; Pey���//U Sample pts: 100; Km,�*)X.-5 相干光; �&pM'$}T* 波长0.5876微米, ���I:i<>kG 距离原点沿着Z轴负方向25mm。 B| t�zF0;c �?4 �qkDtm 对于执行代码,如果想保存图片,请在开始之前一定要执行如下代码: bp#fy�G"� enableservice('AutomationServer', true) ~AQ>g�#|�% enableservice('AutomationServer') QQ�F�f�5^� QQ�F�f�5^�
|