| infotek | 2022-01-24 09:30 |
十字元件热成像分析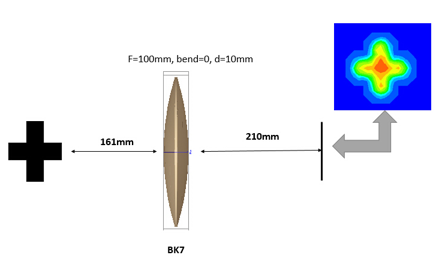 成像示意图 首先我们建立十字元件命名为Target  创建方法: 面1 : 面型:plane 材料:Air 孔径:X=1.5, Y=6,Z=0.075,形状选择Box 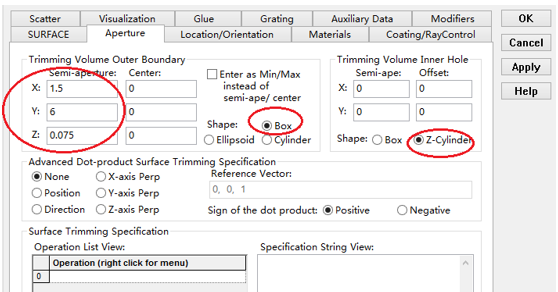 首先在第一行输入temperature :300K, emissivity:0.1; 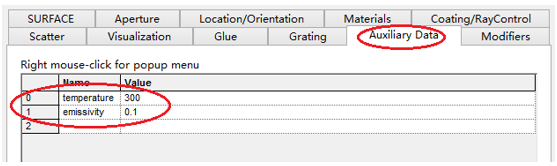 面2 : 面型:plane 材料:Air 孔径:X=1.5, Y=6,Z=0.075,形状选择Box 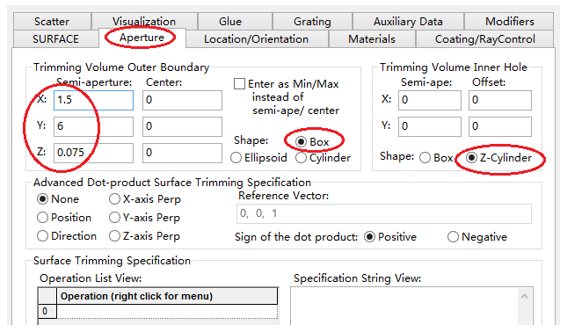 位置坐标:绕Z轴旋转90度, 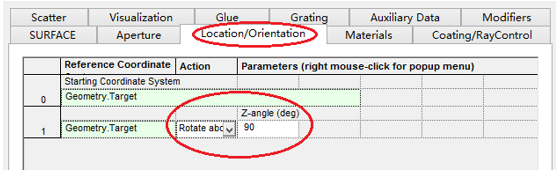 首先在第一行输入temperature :300K,emissivity: 0.1; 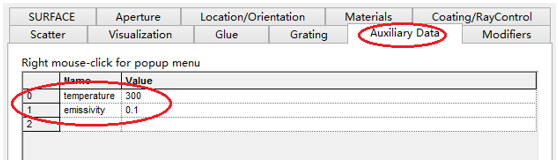 Target 元件距离坐标原点-161mm; 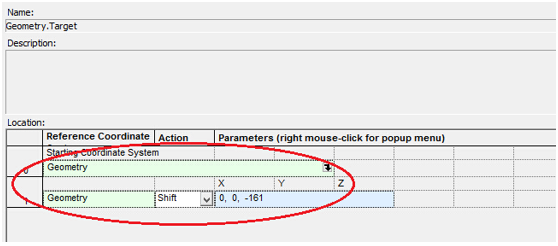  探测器参数设定: 在菜单栏中选择Create/Element Primitive /plane 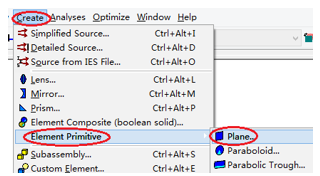 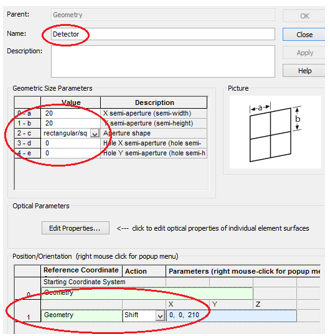 元件半径为20mm*20,mm,距离坐标原点200mm。 光源创建: 光源类型选择为任意平面,光源半角设定为15度。 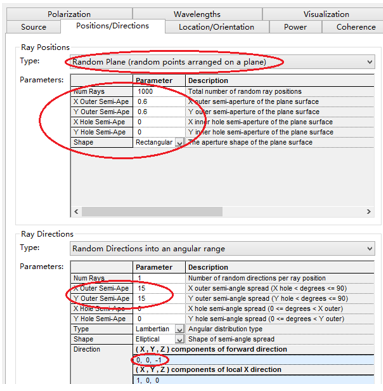 我们将光源设定在探测器位置上,具体的原理解释请见本章第二部分。 我们在位置选项又设定一行的目的是通过脚本自动控制光源在探测器平面不同划分区域内不同位置处追迹光线。 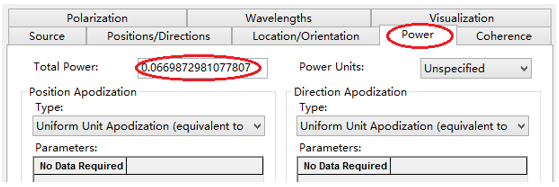 功率数值设定为:P=sin2(theta) theta为光源半角15度。我们为什么要这么设定,在第二部分会给出详细的公式推导。 创建分析面: 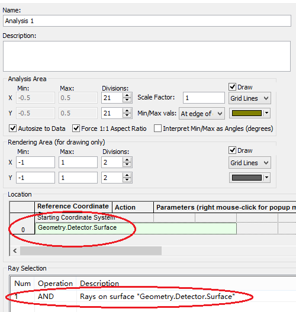 到这里元件参数设定完成,现在我们设定元件的光学属性,在前面我们分别对第一和第二面设定的温度和发射系数,散射属性我们设定为黑朗伯,4%的散射。并分别赋予到面一和面二。 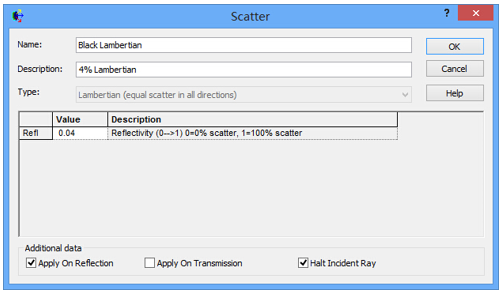  FRED具有一个内置的可编译的Basic脚本语言。从Visual Basic脚本语言里,几乎所有用户图形界面(GUI)命令是可用这里的。FRED同样具有自动的客户端和服务器能力,它可以被调用和并调用其他可启动程序,如Excel。因此可以在探测器像素点上定义多个离轴光源,及在FRED Basic脚本语言里的For Next loops语句沿着探测器像素点向上和向下扫描来反向追迹光线,这样可以使用三维图表查看器(Tools/Open plot files in 3D chart)调用和查看数据。 将如下的代码放置在树形文件夹 Embedded Scripts, 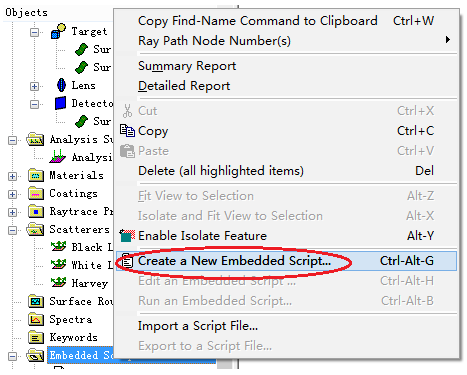 绿色字体为说明文字, '#Language "WWB-COM" 'script for calculating thermal image map 'edited rnp 4 november 2005 'declarations Dim op As T_OPERATION Dim trm As T_TRIMVOLUME Dim irrad(32,32) As Double 'make consistent with sampling Dim temp As Double Dim emiss As Double Dim fname As String, fullfilepath As String 'Option Explicit Sub Main 'USER INPUTS nx = 31 ny = 31 numRays = 1000 minWave = 7 'microns maxWave = 11 'microns sigma = 5.67e-14 'watts/mm^2/deg k^4 fname = "teapotimage.dat" Print "" Print "THERMAL IMAGE CALCULATION" detnode = FindFullName( "Geometry.Detector.Surface" ) '找到探测器平面节点 Print "found detector array at node " & detnode srcnode = FindFullName( "Optical Sources.Source 1" ) '找到光源节点 Print "found differential detector area at node " & srcnode GetTrimVolume detnode, trm detx = trm.xSemiApe dety = trm.ySemiApe area = 4 * detx * dety Print "detector array semiaperture dimensions are " & detx & " by " & dety Print "sampling is " & nx & " by " & ny 'reset differential detector area dimensions to be consistent with sampling pixelx = 2 * detx / nx pixely = 2 * dety / ny SetSourcePosGridRandom srcnode, pixelx / 2, pixely / 2, numRays, False Print "resetting source dimensions to " & pixelx / 2 & " by " & pixely / 2 'reset the source power SetSourcePower( srcnode, Sin(DegToRad(15))^2 ) Print "resetting the source power to " & GetSourcePower( srcnode ) & " units" 'zero out irradiance array For i = 0 To ny - 1 For j = 0 To nx - 1 irrad(i,j) = 0.0 Next j Next i 'main loop EnableTextPrinting( False ) ypos = dety + pixely / 2 For i = 0 To ny - 1 xpos = -detx - pixelx / 2 ypos = ypos - pixely EnableTextPrinting( True ) Print i EnableTextPrinting( False ) For j = 0 To nx - 1 xpos = xpos + pixelx 'shift source LockOperationUpdates srcnode, True GetOperation srcnode, 1, op op.val1 = xpos op.val2 = ypos SetOperation srcnode, 1, op LockOperationUpdates srcnode, False raytrace DeleteRays CreateSource srcnode TraceExisting 'draw 'radiometry For k = 0 To GetEntityCount()-1 If IsSurface( k ) Then temp = AuxDataGetData( k, "temperature" ) emiss = AuxDataGetData( k, "emissivity" ) If ( temp <> 0 And emiss <> 0 ) Then ProjSolidAngleByPi = GetSurfIncidentPower( k ) frac = BlackBodyFractionalEnergy ( minWave, maxWave, temp ) irrad(i,j) = irrad(i,j) + frac * emiss * sigma * temp^4 * ProjSolidAngleByPi End If End If Next k Next j Next i EnableTextPrinting( True ) 'write out file fullfilepath = CurDir() & "\" & fname Open fullfilepath For Output As #1 Print #1, "GRID " & nx & " " & ny Print #1, "1e+308" Print #1, pixelx & " " & pixely Print #1, -detx+pixelx/2 & " " & -dety+pixely/2 maxRow = nx - 1 maxCol = ny - 1 For rowNum = 0 To maxRow ' begin loop over rows (constant X) row = "" For colNum = maxCol To 0 Step -1 ' begin loop over columns (constant Y) row = row & irrad(colNum,rowNum) & " " ' append column data to row string Next colNum ' end loop over columns Print #1, row Next rowNum ' end loop over rows Close #1 Print "File written: " & fullfilepath Print "All done!!" End Sub 在输出报告中,我们会看到脚本对光源的孔径和功率做了修改,并最终经过31次迭代,将所有的热成像数据以dat的格式放置于:  找到Tools工具,点击Open plot files in 3D chart并找到该文件  打开后,选择二维平面图: 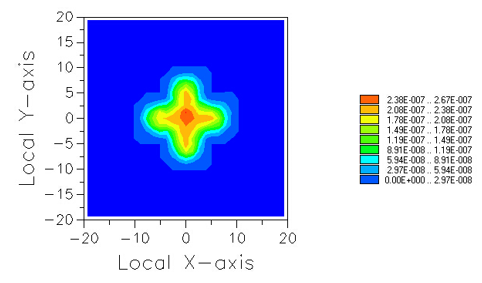 |
|