SYNOPSYS 光学设计软件课程十三:带有Kinoform镜头的激光扩束器
+rX�F{@
�l
��~EzaC?fQ
在第11课中,您了解了如何使用普通球面透镜设计激光扩束器,并了解到需要多个透镜元件才能获得良好的性能。 第12课采用相同的设计,使用两个非球面元件,效果极佳。 本课程将证明您可以使用DOE(衍射光学元件)。 X-LA}YH=tS
目标是将腰半径为0.35mm的HeNe激光器转换成直径为10mm且均匀至10%以内的光束。 )D&M2CUw"f
这是我们初始的输入文件: V/d/L�3p��
RLE ! Beginning of lens input file. 。 >E�sz�iRm
ID KINOFORM BEAM SHAPER i�_R����e*
WA1 .6328 ! Single wavelength �Z?P�~�z07
UNI MM ! Lens is in millimeters W���La!.v>
OBG .35 1 ! Gaussian object; waist radius -.35 mm; define full aperture = 1/e**2 point. +!IQj0&'Y3
1 TH 22 ! Surface 2 is 22 mm from the waist . }A=y�=+4�j
2 RD -2 TH 2 GTB S ! Guess some reasonable lens parameters; use glass type SF6 from Schott catalog I){�\0v�b@
SF6
�-t�2T(ha
3 TH 20 ! Surface 3 is a kinoform on side 2 of the first element
|{�r$jZeE
3 USS 16 ! Defined as Unusual Surface Shape 16 (simple DOE) }R[#?ty;�]
CWAV .6328 ! Zones are defined as one wave phase change at this wavelengt dy__e��^qi
HIN 1.7988 55 ! Assume the zones are machined into the lens. You can also apply ! a film of a different index. ��fWc�|g�q
RNORM 1 $r�F=_D6�
2&��'|Eqk�
4 TH 2 GTB S ]u��j=�:�@
SF6 `;���|5��
4 USS 16 IQ<��My�B(
CWAV .6328 aNn"X y\ k
HIN 1.7988 55 �T�<��3�BT
RNORM 1 $
,SF@�BhO
! The first side of the second element is also a DOE Rlnb�db;!k
5 CV 0 TH 50 ! Start with a flat surface U[L9�*=�P;
7 ! Surfaces 6 and 7 exist oI:o"T77sA
AFOCAL ! because they are required for AFOCAL output. zya5Jb:S�g
END ! End of lens input file. Ji1Pz�)fq�
-�oe�L�{9;
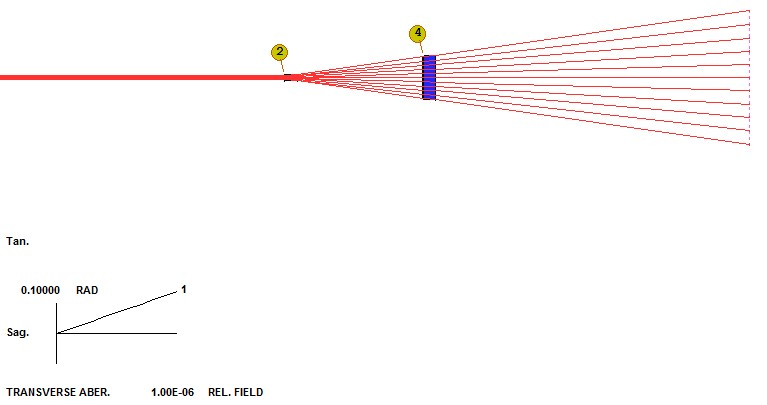
我们给第2个表面指定了一个合理RD值。 这是现阶段还没有DOE的非球面系数的系统: 0~wF�3B�gV
光束被扩展但没有准直,并且强度分布仍然是高斯输入光束的强度分布。 任务是找到能够实现我们两个目标的DOE OPD目标。 首先,让我们将第二个透镜的两边保持为平面。 这是优化MACro: �/={���Js*
PANT ! Start of variable parameter definitions. 7!��,YNy%
RDR .001 ! This is a very small beam, so use smaller derivative increments to start with VY X"gCR�n%tn
2 RAD '�i;��|�c�
VLIST TH 3 ! Vary the airspace !C�gx�.� �
VY 3 G 26 ! Vary term Y**2, <!-sZ_q��q
VY 3 G 27 ! Y**4, �]5~s�"fnG
VY 3 G 28 ! and Y**6 ?Xdak�|?�i
�sDr/k`>��
VY 4 G 26 ! Do the same at surface 4 �ta��GU��
VY 4 G 27 [ EFMu�;q�
VY 4 G 28 S�p�o?i.#
�Zwcy4�>�8
END |@�,|F:h<M
����j'[m:/
AANT ! Start of merit function definition c�_a��Z{S�
AEC iGB_{F~t4}
ACC CT0l!J~5m~
LUL 150 1 1 A TOTL ! Prevent the system from growing too large mk�7&�<M��
M 5 1 A P YA 0 0 1 0 5 ! Ask for a beam radius of 5 mm on surface 5 ��[7(-�T?_
kGpa\c
�g1
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 1 0 6 ! Ask for a flux falloff of zero at several zones �PB%�-9C0�
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .98 0 6 q~C�A0�A�R
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .97 0 6 qq)0yyL r�
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .96 0 6 �m)V�/�L]4
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .95 0 6 y�4h=Lki@�
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .94 0 6 �*Av�"JA�X
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .93 0 6 #;n�+YM">:
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .92 0 6 [I4�ege>��
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .91 0 6 gaA<}Tp,��
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .85 0 6 9/+Nj���/
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .8 0 6 �o6f_l^�+H
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .7 0 6 ^F?&|c�lM/
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .5 0 6 �E?(xb �B�
M 0 1 A P FLUX 0 0 .3 0 6 �e8�YMX&0%
GSO 0 .1 10 P ! Control the output ray OPD over an SFAN of 10 rays, S'�oGt�&Z<
GSR 0 100 10 P ! and some transverse aberrations too. �t�m7�u^9]
END ! End of merit function definition. 3@5=+z�~CW
SNAP 2[0JO.K
4�
SYNO 40 iU6Gp-<M�,
8|E'>+ D_-
这个PANT文件改变了一些通用的G变量,我们在上一课中使用它来改变镜头元件上的一些非球面系数项。 但在这种情况下,表面已经被定义为USS类型16,这是一个简单的DOE表面,因此这些选项改变了定义该形状的系数。 (键入HELP USS以了解您可用的形状以及G系数如何应用于它们。) �e><�5Pr�)
我们运行这个宏,镜头看起来很有希望。 所以我们再次运行它然后模拟退火几个周期。 BBcV9CGU
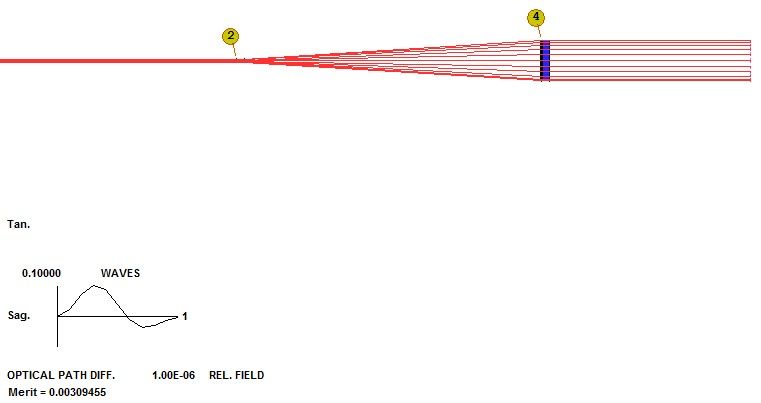
结果变得更好了。 我们尝试改变一些高阶系数。 我们在两个DOE上添加新系数,最高为G 31,即Y ** 12系数。 重新优化后,镜头看起来大致相同,但评价函数下降到3.13E-7。 看起来结果收敛了! Ax�!+P\\2~
光通量如何随孔径变化? 我们输入命令 Sa19�q.~�%
FLUX 100 P 6 0%!rx{f#�\
b64
@s�2�]
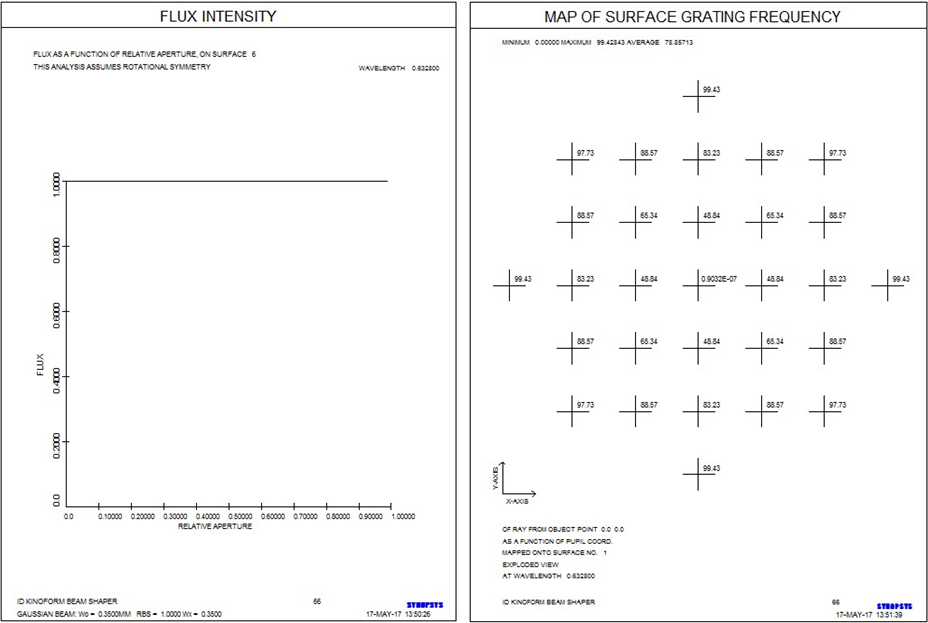
并得到一条美丽的曲线,几乎是直的,显示在左下方。 �JCA�q8=zM
这确实是一个很好的设计。 现在的问题是,可以被加工吗? 表面4的空间频率是多少? 如果它太高,制造技术可能会遇到麻烦。 我们打开MMA对话框以选择MAP命令的输入。 我们选择一个HSFREQ over PUPIL的图,对象为POINT 0,而raygrid CREC的网格为7,DIGITAL输出和PLOT。 结果显示在镜片边缘右侧,下方的频率为99.43 c / mm。 cb5�,�P~/q
10微米/周期,这是可以制作的,但不容易被加工。 我们可以减少到50 c / mm吗? 我们将变量5 RAD添加到变量列表中,并为AANT文件添加新的像差: Xf)|�P��u
M 50 .01 A P HSFREQ 0 0 1 0 4 f��|u#2�!7
{'16:�dTJ�
程序现在控制表面4上的频率。我们重新优化,现在表面5略微凸起,4上的空间频率正好在50 c / mm。 光通量均匀性与以前一样好。 任务完成! =�]��3tU�D
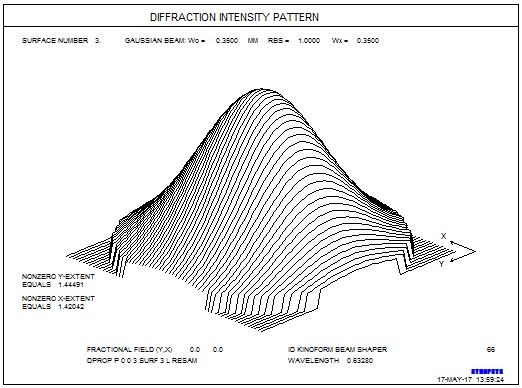
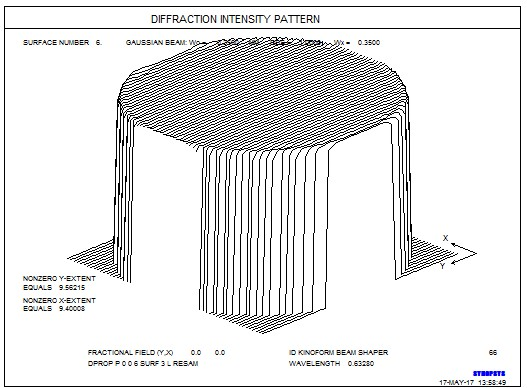
我们做得怎么样? 在光束重构之前,运行DPROP命令,检查曲面3处的轮廓。 这显示了该点处光束的高斯分布。 r>�bJ%M�}�
DPROP P 0 0 3 SURF 3 L RESAMPLE 6_N(;6k�x(
Kx_h���1{�
现在在表面上6做同样的事情。 �K'�t]n�{$
DPROP P 0 0 6 SURF 3 L RESAMPLE 5k|9gICyd*
�/b|��0PMX
下面是生成的系统的RLE文件,如果评估它,可以将其复制并粘贴到编辑器中: ��8�w({\=�
RLE p�m{|�?�R�
ID KINOFORM BEAM SHAPER u&�wi�GwF[
FNAME 'L13L1.RLE ' Zo>]�rKeV�
MERIT 0.270980E-05 �?f/�n0U4w
WA1 .6328000 =_Y���G#yS
WT1 1.00000 �*,Bzc�Z��
APS 1 �(k�np#���
AFOCAL _G�1gtu�]�
UNITS MM ja=F��7Usb
OBG 0.35000000 1.0000000 Zw
wqSyuGf
0 AIR !n^O�M?.�4
1 CV 0.0000000000000 TH 22.00000000 AIR .f+�T�ZDUO
2 RAD -0.8227781050995 TH 2.00000000
]�({~,8�s
2 N1 1.79881710 �Q]p(�u\*
2 CTE 0.810000E-05 l7���De6A"
2 GTB S 'SF6 ' NH��_<q"gT
3 CV 0.0000000000000 TH 74.00214849 AIR ��@3��kKJ
3 USS 16 A�<;S�n�Xm
CWAV 0.632800 v@#�b}N0n�
HIN 1.798800 55.000000 #�n�h�|=X�
RNORM 1.00000 9)VF �1L�D
3 XDD 1 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 O9:U8�$*��
3 XDD 2 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0Ia(�$.1mY
3 XDD 3 2.6875641E+02 5.7065730E+01 -4.1566734E+01 2.8677115E+01 -1.6241740E+01 -�.{�g�}R%
3 XDD 4 4.7211923E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 ZoArQ(YF�y
4 CV 0.0000000000000 TH 2.00000000 A=Ss�6�-Je
4 N1 1.79881710 @?"h
!fyu�
4 CTE 0.810000E-05 r1�fGJv1!o
4 GTB S 'SF6 ' %u;~kP�|S%
4 USS 16 �GKcv<G208
CWAV 0.632800 F5�o+k�z$;
HIN 1.798800 55.000000 2�k<��;R':
RNORM 1.00000 F`9�]=T��0
4 XDD 1 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 �%�6��_AM�
4 XDD 2 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 ��zR�PeNdX
4 XDD 3 5.6803879E+00 -9.1936550E-03 6.0997390E-04 -5.7203063E-05 2.2090382E-06 �0@AA�ulRl
4 XDD 4 -3.5824860E-08 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00 3MRc�4Ul�B
5 RAD -159.6274584523634 TH 50.00000000 AIR
�Y��tO|D
6 CV 0.0000000000000 TH 0.00000000 AIR �W0}B'VS.I
7 CV 0.0000000000000 TH 0.00000000 AIR END
|